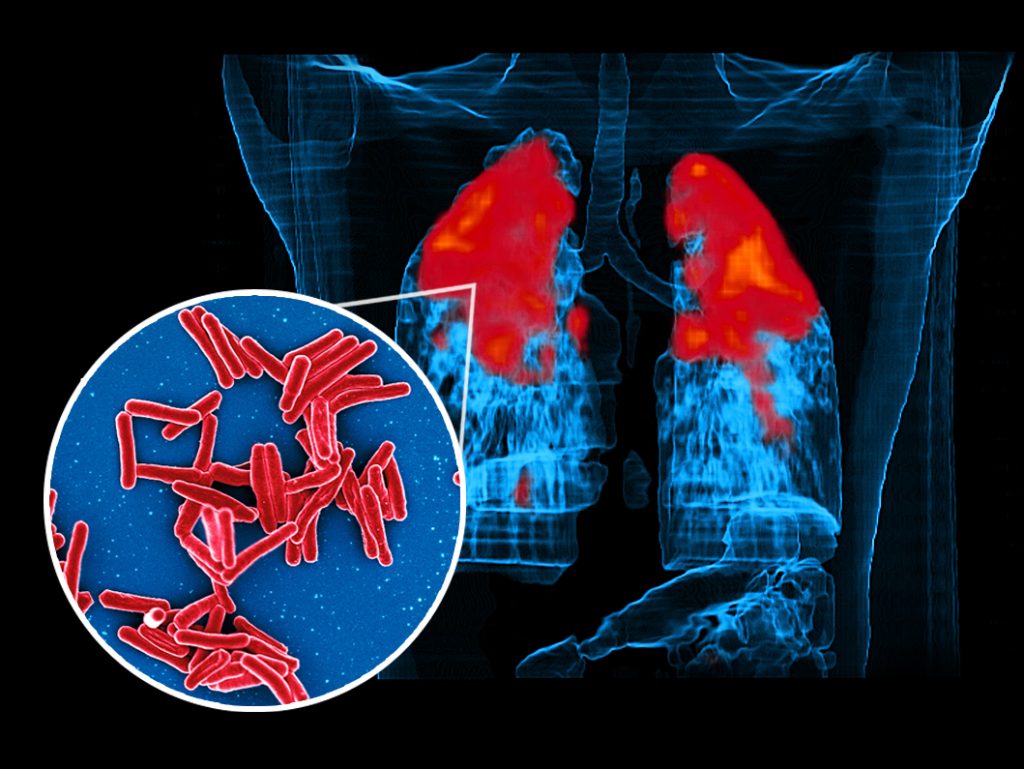
TB, also known as tuberculosis, is an ancient disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. This bacteria usually affects the lymph nodes of the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body, such as the lymph glands, intestines, throat, bones, joints, etc. This is called Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis.
TB can be latent or hidden, which is called Latent TB, while Active TB is called Active TB. In latent TB, the patient has TB germs in his body, but the disease does not spread from that patient to other people, while in active TB, the patient can transmit the germs of this disease to other people. TB germs can also be transmitted by the patient coughing, sneezing, spitting, and sitting near a person and breathing.
This disease affects a healthy person. More than two hundred thousand people in Pakistan suffer from TB every year. Most people living below the poverty line fall prey to this deadly disease because they do not have access to adequate and necessary food, clean water and proper housing. TB also has more opportunities to thrive in dark and cramped environments.
Factors such as old and dirty houses, violation of hygiene rules and substandard food also play an important role in the spread of TB. Apart from this, the chances of this disease spreading also increase in dusty, dusty and muddy environments.
If someone has latent TB, then there are no symptoms until then, but when the disease becomes active, symptoms appear.
Symptoms of active TB include a cough lasting more than three weeks, thick and foul-smelling phlegm with blood, fever, loss of appetite, physical weakness, fatigue, lethargy, weight loss, chest pain, excessive sweating at night, cough with foam and yellowing of the mucus, and sore throat, especially swollen lymph glands. Blood can often be seen in the urine.
The TB germ often enters the body of people, but the body’s immune system fights it off and protects against TB. TB germs are inactive, but they remain alive and can attack and activate the disease when a person’s immune system weakens at any point in life. Latent TB is diagnosed through the tuberculin test, while sputum tests, X-rays, FNAC and PCR, etc. are recommended for the diagnosis of active TB.
After the final diagnosis, the treatment phase begins. If you experience any symptoms of TB, get a sputum test done at your nearest health center or a selected private laboratory. If you contract TB, there is no need to panic, because complete recovery from the disease is possible through treatment under the supervision of the World Health Organization. The National TB Control Program and the World Health Organization have developed a treatment method called DOTS, in which after the disease is diagnosed, the drugs prescribed by a doctor are used continuously for eight months under the supervision of a responsible person without any break.
TB is an infectious but 100 percent curable disease. Among the measures we can implement to control this deadly disease, the first thing we should do is vaccinate the child with BCG after birth. The course of treatment should be completed and not left incomplete. Because in the initial days of treatment, patients start feeling better and leave the course incomplete.
Remember, neglecting treatment can be dangerous. Keep the house clean and eat a balanced, quality diet. Do not keep problems on your mind all the time, because this disease can also be caused by being anxious and worried all the time. The patient should be kept in a comfortable, spacious and calm environment. Keep the patient’s food and drink separate from other members of the house, so that other healthy people can be protected from this disease.
Encourage the patient to get treatment. In addition, the patient should keep a handkerchief or any cloth over his mouth while coughing and sneezing. Also, avoid spitting everywhere. The patient needs physical and mental peace and comfort in this disease. Initially, the patient should be advised to rest until the fever subsides. Eat a good and light diet that is high in protein.
Eggs, milk, yogurt, etc. are the best foods.
TB disease can affect anyone, but risk factors include the patient’s family, friends, people who are not healthy or live in crowded places, people who have lived in countries where the rate of TB is relatively high, such as some countries in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, children of parents whose country of origin has a high rate of TB, people whose immune system is weakened due to HIV disease or treatment for a disease, and people who use drugs and live in unhealthy environments.
A compassionate and friendly attitude towards the patient is essential for recovery, so provide the patient with a pleasant environment and feed them good food.